Adult Flat Foot
Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction and acquired flatfoot
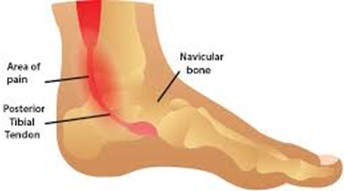
Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction occurs when the tendon that attaches the calf muscle to the bone on the inner part of your foot becomes inflamed or torn.
Tendons connect muscles to bones and stretch across joints, enabling you to bend that joint. The posterior tibial tendon starts in your calf, stretches down behind the inside of your ankle and attaches to bones in the middle of your foot.
When the posterior tibial tendon becomes inflamed, overstretched or torn, you may have symptoms of inner ankle pain. Gradually, you may lose the inner arch on the bottom of your foot, resulting in a condition called "acquired flatfoot".
Symptoms of PTTD
The symptoms of PTTD may include pain, swelling, a flattening of the arch, and an inward rolling of the ankle. As the condition progresses, the symptoms will change and so will the treatment.
Stages of PTTD
-
No. 1
When PTTD initially develops, typically there is pain on the inside of the foot and ankle (along the course of the tendon) accompanied by inflammation and swelling.
-
No. 2
Later, as the arch begins to visibly flatten, there may still be pain on the inside of the foot and ankle. But at this point, the foot and toes begin to turn outward and the ankle rolls inward. During stage 2, your foot should still be quite flexible and able to form an arch when non weight baring.
-
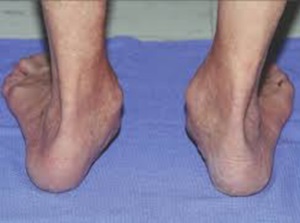
No. 3
As PTTD becomes more advanced, the arch flattens even more and the pain often shifts to the outside of the foot, below the ankle. At this time the foot often becomes a rigid, non movable flat foot, At this point the tendon has deteriorated considerably and arthritis often develops in the foot. In more severe cases, arthritis may also develop in the ankle.
Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction Diagnosis
It is important to undertake a complete medical history and provide a thorough physical examination of your foot and ankle. Checking for swelling, pain and tenderness along the inside of the foot and ankle. Flexibility and range of motion will be tested as well to check for posterior tibial tendon dysfunction. After the physical examination is complete, it it common to order one or more of the following diagnostic imaging tests:
Nonsurgical Treatment
Symptoms will be relieved in most patients with appropriate nonsurgical treatment. Pain may last longer than 3 months even with early treatment. For patients who have had pain for many months, it is not uncommon for the pain to last another 6 months after treatment starts.
Decreasing or even stopping activities that worsen the pain is the first step. Switching to low-impact exercise is helpful. Biking, elliptical machines, or swimming do not put a large impact load on the foot, and are generally tolerated by most patients.
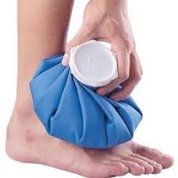
Apply cold packs on the most painful area of the posterior tibial tendon for 20 minutes at a time, 3 or 4 times a day to keep down swelling. Do not apply ice directly to the skin. Placing ice over the tendon immediately after completing an exercise helps to decrease the inflammation around the tendon.
Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatories such as ibuprofen or naproxen, reduce pain and inflammation. Taking such medications about a half of an hour before an exercise activity helps to limit inflammation around the tendon. The thickening of the tendon that is present is degenerated tendon. It will not go away with medication.
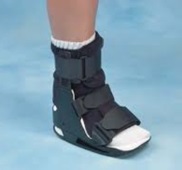
A short leg cast or walking boot may be used for 6 to 8 weeks. This allows the tendon to rest and the swelling to go down. However, a cast causes the other muscles of the leg to atrophy (decrease in strength) and thus is only used if no other conservative treatment works.
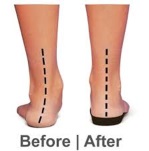
Most people can be helped with orthotics and braces. An orthotic is a shoe insert. It is the most common nonsurgical treatment for a flatfoot. An over-the-counter orthotic may be enough for patients with a mild change in the shape of the foot. A custom orthotic is required in patients who have moderate to severe changes in the shape of the foot. The custom orthotic is more costly, but it allows to better control the position the foot.
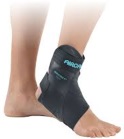
A lace-up ankle brace may help mild to moderate flatfoot. The brace would support the joints of the back of the foot and take tension off of the tendon. A custom-molded brace is needed in severe flatfoot that is stiff or arthritic. The brace can help some patients avoid surgery.
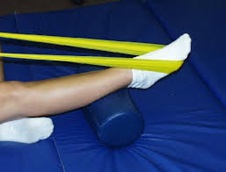
Physical therapy that strengthens the tendon can help patients with mild to moderate disease of the posterior tibial tendon.

Cortisone is a very powerful anti-inflammatory medicine A cortisone injection into the posterior tibial tendon is not normally done. It carries a risk of tendon rupture.